FPX Access Management Overview
What is FPX?
The Federated Privacy Exchange (FPX) product provides authorization and consent management.
FPX consists of several core components: the Authorization Server, Wallet and Navigator, and Resource Servers. These components work together to manage access to a user’s personal information. Another key player, the Client, interacts with FPX on behalf of a digital service provider. The Client and the FPX components are described in the following sections.
Note: In the IDENTOS documentation, a user refers to someone who is receiving services from a digital service provider. For example, a person using a mobile banking app would be a user, and the bank providing the mobile app would be a digital service provider.
Client
The Client is an application, acting on behalf of a digital service provider, that requires access to an individual’s personal information. Examples of Client applications include:
- A mobile app that creates calendar events for upcoming immunizations. In this case, the Client would need to access the person’s immunization history.
- A web app that lets someone check their credit score and offers financial advice. In this case, the Client would need to access the person’s credit score information.
When the Client application needs to access personal information, it sends a request to the Authorization Server. This personal information is called digital resources or just resources.
Client requests may be initiated by an individual who is using a Client application, such as the mobile and web app examples above. Client requests can also result from system processes that don’t involve the direct involvement of an individual. For example, after a Client application gains access via an individual, the Client application may continue to request data to ensure it always has the latest information.
Authorization Server
The Authorization Server is responsible for managing the Client’s access to resources. When the Authorization Server receives a request from the Client, the server performs the following tasks:
- Sends the Client request to the user’s Wallet or Navigator app to ask for the user’s consent to share resources with the Client.
- Uses predefined parameters and policies to determine if the Client is allowed to access the resources they’ve requested.
- Sends a response back to the Client, either approving or denying the Client’s request for resources.
Wallet and Navigator
A digital service provider can use the Wallet and Navigator to provide applications to their users. The Wallet can be used to provide web apps, while the Navigator can be used to provide native mobile apps for Android and iOS. For example, a healthcare provider might use the Navigator to offer patients a mobile app where they can keep track of their immunizations.
The Wallet and Navigator apps allow the user to:
- Create and manage their user account with the digital service provider
- Provide consent for a Client to access their personal information (i.e. resources)
- Select the source (i.e. Resource Server) for the resources that will be shared with the Client
- Revoke consent for a Client to access resources
Resource Server
A Resource Server hosts the resources that the Client wants to access. A resource refers to any kind of digital content.
Resources can include simple items (like PDF files, images, and videos) or more complex items (like customer portals, interactive web pages, and full-service APIs). A common resource requested by a Client is a person’s profile or user information. Other resource examples include a person’s immunization records or medical test results.
Some resources are public and can be accessed by anyone. For example, most websites are public. Other resources are protected and require permission in order to access them. For example, a person’s medical records are protected resources. As discussed in the “Authorization Server” section, a Client must receive authorization before they can access protected resources on a Resource Server.
FPX Access Management Data Flow
The following diagram shows the flow of information between the FPX components. This data flow is initiated when the Client application requests resources, such as a user’s profile or other personal information.
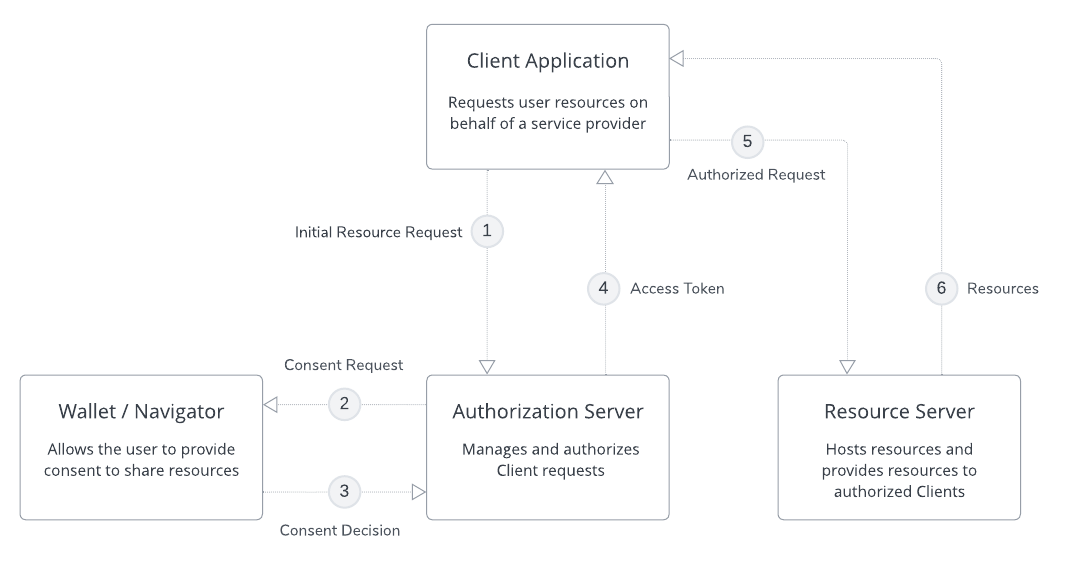
FPX Access Management Data Flow
1. Client Request Resources
The Client sends a request to the Authorization Server asking for access to resources. The Client application requires this information in order to provide a service for the user.
Example: June Smith wants to use a mobile app called “My Immunizations” to check their immunization history. June Smith signs into the app for the first time. The “My Immunizations” app sends a request to the Authorization Server asking for June Smith’s immunization records.
2. Authorization Server Requests User Consent
The Authorization Server sends the Client request to the user’s Wallet or Navigator app. The user reviews the request and decides if they will allow the Client to access the requested resources. If the resources are available on multiple Resource Servers, the user may also be able to select where the information will be sourced from.
Example: June Smith receives a notification on their phone asking if the “My Immunizations” app is allowed to access their immunization records. June Smith selects “Yes”, granting consent to the app.
3. Wallet/Navigator Provides User Consent
The Wallet or Navigator app replies to the Authorization Server with the user’s consent and (optionally) the information source selected by the user.
Example: The “My Immunizations” app sends June Smith’s response to the Authorization Server.
4. Authorization Server Authorizes the Client Request
The Authorization Server uses a set of predefined parameters and policies to determine whether the Client is allowed to access the resources they’ve requested. If so, the Authorization Server provides the Client with an access token. The token authorizes the Client to access specific resources and scopes.
Example: The Authorization Server determines that the “My Immunizations” app is allowed to view June Smith’s immunization records. The Authorization Server sends an access token to the “My Immunizations” app.
5. Client Requests Authorized Resources
Using the access token provided by the Authorization Server, the Client sends a request to the Resource Server. This request specifies the resources that the Client is authorized to access.
Example: The “My Immunizations” app uses the access token to call the Resource Server where June Smith’s immunization records are located.
6. Resource Server Provides Authorized Resources
The Resource Server provides the Client with the resources that they have been authorized to access.
Example: The Resource Server sends June Smith’s immunization records to the “My Immunizations” app. June Smith can now view their immunization history in the app.
User Privacy
It’s important to note that FPX manages access to information, not the information itself.
FPX obtains user consent to share information and authorizes a Client to access specific resources. FPX connects the Client with the Resource Server hosting the requested resources and the resources are transferred directly from the Resource Server to the Client. This ensures user privacy is maintained at all times.